Introduction to ADA Compliance: Unveiling the Significance and Basic Requirements of the Americans with Disabilities Act

The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), enacted in 1990, stands as a landmark civil rights law. It aims to safeguard individuals with physical and mental disabilities from discrimination across various public life sectors, ensuring equal rights and opportunities for all. This comprehensive legislation is divided into five titles, each addressing a different aspect of public and private life.
What is the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)?
The ADA prohibits discrimination based on disability, ensuring that individuals with disabilities enjoy the same rights and opportunities as everyone else. It covers areas like employment, state and local government services, public accommodations, telecommunications, and transportation.
Major Life Activities as Defined by the ADA
The ADA extends its protection by defining major life activities, which include daily functions like eating, sleeping, walking, and cognitive tasks such as thinking and communicating. It also covers the operation of major bodily functions.
ADA Compliance Firm
Understanding the Five Titles of the ADA
- Title I – Employment: This section applies to employers with 15 or more employees and mandates equal employment opportunities, including reasonable accommodations for individuals with disabilities.
- Title II – Public Services (State and Local Government): It prohibits discrimination by public entities and requires all government programs and services to be accessible to individuals with disabilities.
- Title III – Public Accommodations and Services Operated by Private Entities: This title ensures accessibility in places of public accommodation, such as hotels, restaurants, and retail stores, requiring them to accommodate people with disabilities effectively.
- Title IV – Telecommunications: It mandates telephone and internet companies to provide services that enable individuals with hearing or speech disabilities to communicate over the phone.
- Title V – Miscellaneous Provisions: This section contains various provisions related to the ADA as a whole, including its relationship with other laws and provisions against retaliation and coercion.
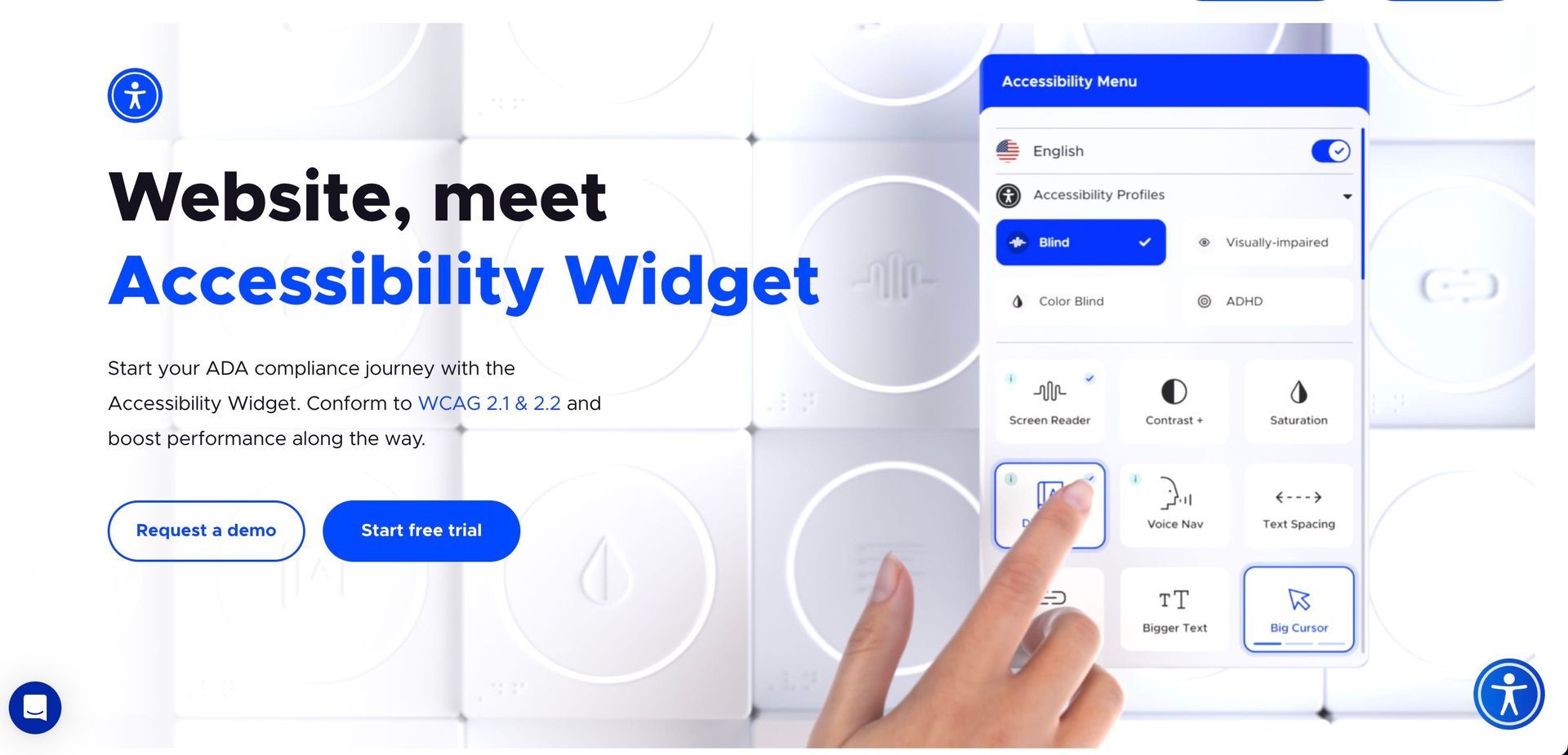
Digital Accessibility under the ADA
With the digital age’s advancement, ADA compliance has extended to digital platforms. The DOJ has clarified that websites and digital platforms fall under ADA coverage, especially those in the public sector. Non-compliance can lead to legal implications, emphasizing the importance of making digital content accessible to everyone, including those with disabilities.
Compliance Strategies and Challenges
Achieving ADA compliance involves familiarizing with standards like WCAG and Section 508, conducting accessibility audits, and regular training for web developers. Challenges include a lack of awareness and technical complexities in retrofitting existing websites. A proactive approach, including regular updates and engagement with accessibility experts, is crucial for ongoing compliance.
Navigating ADA Compliance in the Workplace
Under Title I of the ADA, employers with 15 or more employees are mandated to provide equal employment opportunities to individuals with disabilities. This includes not only hiring but also job training, promotions, and other employment-related activities. Employers are required to make reasonable accommodations for employees with disabilities, unless doing so would cause undue hardship.
Key Steps for Employers:
- Understanding Legal Obligations: Familiarize yourself with the ADA requirements related to employment.
- Creating an Inclusive Environment: Implement policies and practices that support diversity and inclusion in the workplace.
- Providing Reasonable Accommodations: Make necessary adjustments to facilitate the employment of individuals with disabilities.
ADA and State and Local Government Services (Title II)
Title II of the ADA covers all activities of state and local governments, ensuring they provide equal opportunities to individuals with disabilities. This includes access to public education, transportation, healthcare, social services, courts, voting, emergency services, and town meetings. It’s crucial for government entities, regardless of size or federal funding, to comply with these requirements.
Actions for Compliance:
- Program Accessibility: Ensure that all government programs and services are accessible.
- Effective Communication: Provide appropriate aids and services to ensure communication with individuals with disabilities is as effective as communication with others.
- Physical Accessibility: Ensure newly constructed or altered facilities are accessible.
Title III – Public Accommodations and Services by Private Entities
Businesses and nonprofits serving the public fall under Title III of the ADA. This includes a wide range of establishments like restaurants, hotels, retail stores, movie theaters, schools, day care centers, recreation facilities, and doctor’s offices. These entities must provide equal access to their goods and services to people with disabilities.
Guidelines for Businesses:
- Barrier Removal: Modify facilities to eliminate physical barriers where readily achievable.
- Policy Modifications: Make necessary changes to policies and procedures to accommodate individuals with disabilities.
- Effective Communication: Ensure communication with people having hearing, vision, and speech disabilities is effective.
Title IV – Telecommunications
Title IV of the ADA requires telephone and internet companies to provide telecommunications relay services nationwide. This ensures that individuals with hearing or speech disabilities can communicate over the telephone. Additionally, it mandates closed captioning of federally funded public service announcements.
Implications for Telecommunication Companies:
- Relay Services: Implement and maintain services that enable voice-to-text and text-to-voice communication.
- Closed Captioning: Ensure that public service announcements include accurate and accessible closed captioning.
Title V – Miscellaneous Provisions
This title includes various provisions relating to the ADA as a whole, such as its relationship to other laws, state immunity, impact on insurance providers, prohibition against retaliation, and more. It also lists conditions that are not considered disabilities under the ADA.
Overcoming Challenges in ADA Compliance
Organizations often face challenges in understanding and implementing ADA compliance. To overcome these challenges, businesses and government entities must invest in training and resources, adopt an inclusive design approach from the outset, and stay updated with evolving technologies and standards. Regular collaboration with accessibility experts and engagement in accessibility testing are crucial for ongoing compliance and inclusivity.
Exploring the Impact of ADA on Digital Accessibility
The Rising Importance of Web Accessibility
With the proliferation of digital technology, web accessibility has become a critical aspect of ADA compliance. Businesses, governments, and organizations must ensure that their digital content is accessible to individuals with disabilities. This includes websites, mobile apps, and all forms of digital media. The goal is to provide equal access to online information and services for people with disabilities, such as those with visual, auditory, or motor impairments.
Key Aspects of Digital Accessibility Under the ADA:
- Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG): These guidelines provide a framework for making web content accessible. They are organized around four principles — Perceivable, Operable, Understandable, and Robust (POUR) and define three levels of conformance: A, AA, and AAA.
- Section 508 Compliance: This part of the Rehabilitation Act requires federal agencies and their contractors to make their electronic and information technology accessible.
- Ongoing Compliance: Ensuring ADA compliance in the digital space is an ongoing process, involving regular audits, user testing, and updates to keep pace with technological advancements.
ADA Compliance: Beyond Legal Obligation to Social Responsibility
ADA Compliance as an Ethical Imperative
In today’s society, ADA compliance transcends legal requirements, embodying a commitment to inclusivity and ethical business practices. Organizations are increasingly recognizing the importance of making their services accessible to all, regardless of physical or mental abilities. This shift reflects a growing awareness of the rights of individuals with disabilities and a broader understanding of social responsibility.
Strategies for Cultivating an Inclusive Culture:
- Training and Awareness: Regular training sessions for staff on ADA requirements and inclusive practices.
- Inclusive Design Principles: Incorporating accessibility features from the initial design stages of products and services.
- Engagement and Feedback: Actively engaging with individuals with disabilities to receive feedback and make necessary improvements.
ADA Compliance and the Future
Looking Ahead: ADA Compliance in an Evolving World
As technology continues to advance, ADA compliance will play an increasingly vital role in shaping inclusive and accessible environments. The future will likely see further integration of accessibility features in new technologies and a greater emphasis on universal design principles.
Anticipated Developments:
- Advancements in Assistive Technologies: Emerging technologies, such as AI-driven tools, could offer innovative solutions for enhancing accessibility.
- Broader Legal Interpretations: Legal frameworks may evolve to encompass a wider range of disabilities and accessibility requirements.
- Increased Public Awareness: Ongoing efforts to raise public awareness about the importance of ADA compliance and inclusivity.
ADA compliance is not just a legal requirement but a reflection of an organization’s commitment to equality, inclusivity, and social responsibility. As we move forward, it is imperative for all sectors to embrace these principles, ensuring that everyone, regardless of their abilities, has equal access to opportunities and services.
ADA Compliance: A Pathway to Innovation and Improved User Experience
ADA compliance, particularly in digital spaces, is not just about adhering to legal standards; it’s an opportunity for innovation. By focusing on accessibility, organizations can discover new ways to enhance user experience, reach wider audiences, and improve overall service quality. Accessibility-driven innovations often lead to more intuitive, user-friendly designs that benefit all users, not just those with disabilities.
Examples of Innovation Through Accessibility:
- Voice Recognition Technology: Enhanced voice recognition systems aid users with visual or motor impairments.
- Improved Navigation Features: Developing more intuitive website navigation benefits everyone, especially those with cognitive disabilities.
- Advanced Captioning and Audio Descriptions: These features not only assist those with hearing or visual impairments but also enhance the experience for users in sound-sensitive environments.
The Role of ADA in Fostering Diversity and Inclusion
The ADA has been instrumental in promoting diversity and inclusion in various sectors. By requiring organizations to accommodate individuals with disabilities, it has fostered an environment where diversity is valued and inclusion is a standard practice. This shift towards inclusivity has broad implications, from employment to customer service, impacting how organizations interact with all stakeholders.
Benefits of a Diverse and Inclusive Environment:
- Increased Creativity and Innovation: Diverse teams bring a variety of perspectives, leading to more creative and innovative solutions.
- Broader Market Reach: Inclusive practices enable organizations to connect with a wider audience, including the disability community.
- Enhanced Reputation and Brand Loyalty: Companies known for their commitment to diversity and inclusion often enjoy a positive reputation and greater customer loyalty.
ADA Compliance: A Continuous Journey of Learning and Adaptation
Evolving with Changing Standards and Technologies
ADA compliance is an ongoing journey that requires continuous learning and adaptation. As technologies evolve and standards change, organizations must remain agile, updating their practices and policies to ensure ongoing compliance and inclusivity. This journey is not just about meeting legal requirements but about being proactive in creating environments where all individuals can thrive.
Key Components of an Effective ADA Compliance Strategy:
- Continuous Education: Staying informed about the latest developments in ADA standards and accessibility technologies.
- Regular Audits and Assessments: Conducting routine checks to identify and address potential accessibility issues.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Collaborating with people with disabilities and experts in the field to gain insights and feedback.
Conclusion: Embracing ADA Compliance as a Core Value
The Future is Accessible
Looking ahead, the principles of ADA compliance will continue to shape a more inclusive and accessible world. Embracing these principles as core values is crucial for businesses, governments, and organizations committed to equality and social responsibility. By doing so, they not only comply with legal requirements but also contribute to building a society where diversity is celebrated, and every individual has the opportunity to participate fully.
In conclusion, ADA compliance is more than a legal mandate; it’s a reflection of an organization’s dedication to creating an equitable and inclusive environment for all. As we progress, this commitment will play an increasingly significant role in shaping a future where accessibility is not an afterthought but a fundamental aspect of every design and policy.
These impact levels underscore the broad-ranging benefits of ADA compliance, extending beyond legal requirements to enhancing overall business performance and societal engagement.
ADA compliance is a continuous process that extends beyond legal adherence. It embodies a commitment to inclusivity, equality, and social responsibility. As technology and societal norms evolve, so does the imperative to ensure accessibility for all individuals, regardless of their disabilities.
Reflecting on the surge in digital accessibility lawsuits, the importance of ADA compliance in digital spaces is not just a legal mandate but also a vital aspect of ethical business practice. As technology evolves, so does the need for accessible digital platforms for individuals with disabilities.
Common Questions and Answers about ADA Compliance
Can you explain what the ADA is and its primary purpose?
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) is a civil rights law enacted in 1990 in the United States. Its primary purpose is to prohibit discrimination against individuals with disabilities in all areas of public life, including jobs, schools, transportation, and all public and private places open to the general public. The goal is to ensure that people with disabilities have the same rights and opportunities as everyone else.
Which organizations or businesses are required to comply with ADA regulations?
ADA compliance is required for all private employers with 15 or more employees, state and local governments, employment agencies, labor unions, and businesses operating for the benefit of the public. This includes a wide range of entities like schools, transportation services, retail stores, restaurants, and other public accommodations.
What does the term ‘reasonable accommodation’ mean in the context of ADA compliance?
A ‘reasonable accommodation’ under the ADA refers to necessary and appropriate modifications or adjustments not imposing an undue hardship on the operation of the business. This could include making existing facilities accessible, job restructuring, modifying work schedules, acquiring or modifying equipment, and providing qualified readers or interpreters. The aim is to provide equal employment opportunities to individuals with disabilities.
What are the requirements for digital content under the ADA?
Under the ADA, digital content such as websites, mobile applications, and online resources must be accessible to individuals with disabilities. This includes ensuring that digital platforms are navigable and usable by people with various disabilities, like visual, auditory, motor, or cognitive impairments. Compliance often involves following the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) to ensure digital content is perceivable, operable, understandable, and robust for all users.
Join our newsletter
Recent Blog Posts