Digital Accessibility Compliance: Ensuring Inclusive Online Experiences

In a world where the digital space is expanding at an unprecedented rate, ensuring that your online platform is accessible to everyone isn’t just an ethical choice—it’s also a legal one, with the potential to significantly impact your business. For web developers, compliance officers, and digital marketers, understanding digital accessibility is paramount, not only as a means to avoid legal repercussions but also to create a web that is truly open to all. This comprehensive exploration of digital accessibility compliance will arm you with the knowledge and tools you need to create a more inclusive digital environment, all while boosting the reach and effectiveness of your online presence.
Introduction
The internet is a fundamental part of modern life. Whether it’s for shopping, job-hunting, or learning, more and more of our daily interactions occur online. This makes digital accessibility—the practice of designing websites and digital services that can be used by people with disabilities—absolutely critical. Moreover, ensuring digital accessibility compliance is directly tied to providing an inclusive user experience and is increasingly governed by stringent legal requirements.
In this guide, we delve into the details of digital accessibility compliance to equip professionals with a deep understanding of its significance and implementation. From demystifying regulations to providing a toolkit of best practices, this is a comprehensive roadmap to a digitally inclusive world.
Understanding Digital Accessibility
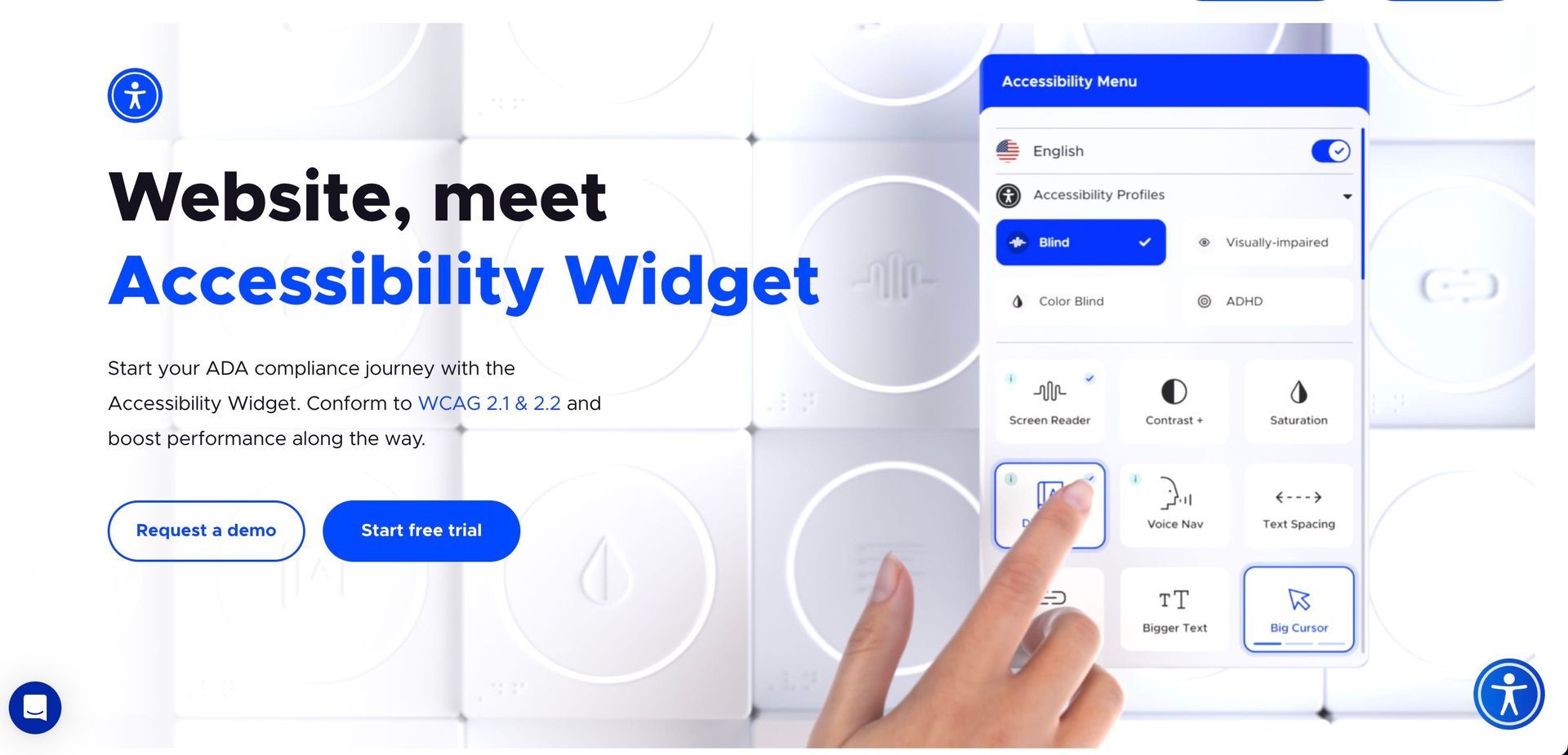
Digital accessibility allows individuals with disabilities to access and interact with digital content. This engagement must be comparable to that of a person without a disability in terms of ease of use and satisfaction. It goes beyond simply providing information, emphasizing the need for engaging experiences that cater to all users.
Key Concepts and Considerations
Among the fundamental concepts of digital accessibility are perceptibility, operability, understandability, and robustness (known as POUR). These concepts guide developers to create websites that can be perceived in multiple ways, operated without demanding precise timing, are easy to understand, and are compatible with a wide range of user agents and assistive technologies.
What’s at Stake?
Failing to accommodate diverse user needs can result in excluding a significant portion of your potential audience. The consequences range from lost sales and reduced traffic to severe legal penalties and damage to reputation.
Legal and Regulatory Landscape
Digital accessibility legislation varies by region, but the common goal is to ensure that people with disabilities are not disadvantaged when accessing information and services online. We’ll examine landmark laws such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) in the U.S., the Disability Discrimination Act (DDA) in the UK, and other international standards to give you a comprehensive understanding of what compliance entails.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
The penalties for failing to meet accessibility standards can be substantial, not just in terms of fines but also in the costs related to redesigning websites, legal fees, and loss of customer trust. Several case studies underscore the importance of taking accessibility regulations seriously.
Common Accessibility Issues
For individuals with visual impairments, navigating the web can be challenging. We’ll detail the accessibility features that can significantly improve their online experience, including screen readers, braille displays, and screen magnifiers.
Hearing Impairments: Ensuring an Auditory Alternative
The web is a multimedia-rich environment, often relying on audio elements. To accommodate those with hearing impairments, understand the critical role of captions and transcripts in accessibility.
Motor and Dexterity Impairments: Facilitating Navigation and Control
Many users have motor impairments that limit their ability to use a mouse or keyboard effectively. Explore the necessary adaptations to allow for use of alternative inputs such as voice commands and switches.
Cognitive Impairments: A Focus on Readability and Clarity
Cognitive disabilities can impact comprehension and focus. Discover guidelines for simplifying complex language, streamlining navigation, and reducing distractions to facilitate engagement.
Best Practices for Digital Accessibility Compliance
Learn about various design elements and development practices that enhance accessibility, from the choice of color contrasts to the structuring of the HTML for a cohesive experience. Understand the significance of semantic HTML, alt attributes on images, and proper form labeling in creating an accessible site.
Content Is King: Creating Accessible Information
Accessibility isn’t just about design and development—it’s also about content. Crafting accessible text, providing clear instructions, and ensuring videos and other multimedia have accompanying text alternatives are key to an inclusive content strategy.
Testing and Continuous Improvement
The testing phase is critical for ensuring compliance. We’ll review different testing methods, including automated tools, manual testing, and user testing with individuals who have disabilities. Moreover, digital accessibility is not a one-time project—it’s an ongoing commitment. Understand the metrics to track and the iterative processes necessary to maintain and improve accessibility over time.
Tools and Resources for Compliance
Discover a range of tools that can automate the detection of many accessibility issues, providing a starting point for compliance efforts.
Assistive Technologies for Testing and Usage
Explore the various software and devices that can help mimic the user experiences of individuals with disabilities, giving you an insight into the accessibility of your digital products.
Training and Certification Programs
Investing in training for your team can be a powerful ally in your quest for accessibility. We’ll explore the available programs, from workshops on disability awareness to certification in web accessibility.
Benefits of Digital Accessibility Compliance
User Experience and Satisfaction
Creating an accessible online presence has the immediate benefit of providing a better user experience. A website that is user-friendly for those with disabilities often results in a more intuitive and efficient experience for all users.
Market Share and Reach
By making your digital platform accessible, you’re casting a wider net. Learn how accessibility can increase your user base and reduce the risk of excluding potential customers.
SEO and Beyond
Digital accessibility is not only good for users; it’s also good for search engine optimization (SEO). We’ll dissect how accessibility practices align with SEO guidelines, improving your website’s visibility and discoverability.
Case Studies
Microsoft: A Trailblazer in Digital Accessibility
Microsoft’s commitment to making technology accessible for everyone is evident in its comprehensive approach, which includes product design, innovation, and partnerships. Their practices are instructive for organizations of any size.
Banking on Inclusion: The Barclays Example
Barclays’ story is one of proactive investment in digital accessibility, illustrating how an accessible online presence can become a competitive advantage in the finance sector.
Amazon: Delivering on the Promise of Universal Access
Amazon’s accessibility initiatives extend to various arms of their business, from the website to their popular devices such as the Kindle. By embracing accessibility, Amazon showcases the power of a universally accessible user experience.
Conclusion
Digital accessibility compliance is a multifaceted endeavor that spans design, technology, and ongoing commitment. By integrating these accessibility best practices into your digital strategy, you will not only be complying with laws and regulations but also fostering an inclusive and engaging online experience for all users. The journey toward accessibility may seem daunting, but the benefits for your users and your business are immeasurable.
As we’ve seen, accessibility compliance is not just a legal checkbox; it’s a value that can profoundly impact your brand’s reputation and reach. It’s time to take the next steps towards digital inclusivity.
Incorporate these practices into your approach, and you’ll be at the forefront of an increasingly important movement in the digital world. Whether you’re a developer, marketer, or a leader within your organization, your efforts in digital accessibility compliance are crucial in building a more inclusive digital community.
Now, with this in-depth guide and an arsenal of strategies at your disposal, it’s your turn to commit to digital accessibility and pave the way for an online environment that genuinely serves the diversity of its users.
Join our newsletter
Recent Blog Posts